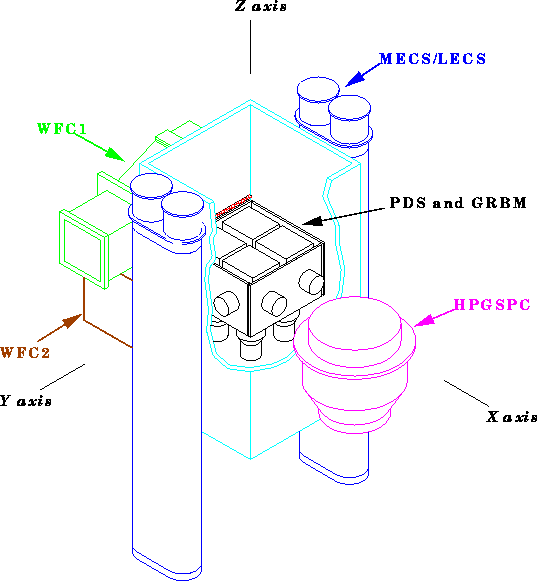
 |
| Instrument | Detecting | Band | FOV | Ang. res. | Eff. Area | Energy Re. |
| units(a) | (keV) | ( |
(arcmin) | (cm2) | (% FWHM) | |
| LECS | 1(+Z) | 0.1-10 | 0.5 | 3.5@0.25 keV | 22@0.25 keV | 8x(E/6)-0.5 |
| MECS | 3(+Z) | 1.3-10 | 0.5 | 1.2@6 keV | 150@6 keV | 8x(E/6)-0.5 |
| HPGSPC | 1(+Z) | 4-120 | 1.1 | collimated | 240@30 keV | 4x(E/60)-0.5 |
| PDS | 1(+Z) | 15-300 | 1.3 | collimated | 600@80 keV | 15x(E/60)-0.5 |
| WFC | 2(-Y,+Y) | 1.5-26 | 20x20 | 3 | 140@10 keV | 18x(E/6)-0.5 |
| GRBM(b) | 4( |
40-700 | open | - | 500@300 keV | 30x(E/100)-0.4 |
The LECS ([Parmar et al. 1997]) and MECS ([Boella et al. 1997b]) units all consists
of grazing incidence X-ray concentrators, composed of 30 nested Nickel Au coated coaxial and co-focal mirrors with a double cone approximation to Wolter I geometry,
and of a gas scintillation proportional counter using Xenon at
about 1.0 atm. The MECS make use of a 50 ![]() m beryllium window
, while the LECS window, in order to extend the energy
band down to 0.1 keV, is made of 1.25
m beryllium window
, while the LECS window, in order to extend the energy
band down to 0.1 keV, is made of 1.25 ![]() m of Polymide, 0.035
m of Polymide, 0.035 ![]() m of aluminum nitride and 0.044
m of aluminum nitride and 0.044 ![]() m of Al. The support structure of the concentrators is made of
carbon fiber tubes an each pair of tubes is contained in a 2cm thick Al box.
m of Al. The support structure of the concentrators is made of
carbon fiber tubes an each pair of tubes is contained in a 2cm thick Al box.
The HPGSPC ([Manzo et al. 1997]) is an high pressure scintillator proportional counter filled with a 5 atm gas mixture (90% Xe and 10% He). The gas cell is cylindrical and made of a Titanium body 3 mm thick and with a diameter of 360 mm and a depth of 184.5 mm. The entrance window is made of two Beryllium foils 0.5 and 0.8 mm thick and has a diameter of 30 cm.
The WFC ([Jager et al. 1997]) consist of two coded aperture cameras, with detector and mask of the same size, about 25.6 x 25.6 cm2. The mask is made of Iron and is located 0.7 m away from the detector, which is a multi wire proportional counter filled with a gas mixture (94% Xe, 5% CO2, 1% He) and with an
entrance window made of
Beryllium 150 ![]() m thick.
The gas cell is made of Titanium coated with 1 mm of Al, and the mask and the detector are
supported by a stainless steel structure. The FOV of the WFC is 20
m thick.
The gas cell is made of Titanium coated with 1 mm of Al, and the mask and the detector are
supported by a stainless steel structure. The FOV of the WFC is 20![]() X 20
X 20![]() FWHM (40
FWHM (40![]() x 40
x 40![]() at zero response).
at zero response).
Finally, The PDS is described in section 1.2, where we outline in detail the GRBM experiment.
The main detecting characteristics of the instruments are reported in Tab. 1.1.