



Next: GRBM on-ground calibrations
Up: The Gamma-Ray Burst Monitor
Previous: The Gamma-Ray Burst Monitor
We can classify the GRBM scientific data products in 3 types:
- 1 s ratemeters:
the
signals detected in each shield between the LLT and the ULT are continuously
counted, with a time resolution of 1 s, and recorded by a proper PDS
housekeeping, the GRBM ratemeter; another housekeeping counter, the AC
ratemeter, records,
for each shield, the count rate detected above the PDS Anti
Coincidence Threshold
(ACT), that is used as a lower level discriminator for any AC signal,
adjustable on 8 steps between nominal 100 and 300 keV. This data are
transmitted to ground in indirect temporal mode; the dead
time is 4
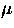 s and the number of bits of the counter is 16 (maximum
number of counts is 65536);
s and the number of bits of the counter is 16 (maximum
number of counts is 65536);
- GRBM PHA spectra: the counts accumulated every 128 s in the GRBM band (LLT-ULT) are
continuously histogrammed on-board in 240 channels spectra by means of PHA
analysis (as described above in the PDS section) and transmitted to ground
in Spectral Indirect Mode; the real number of PHA channels is 256, but channels
from 241 to 256 don't contain scientific data, due to the use of the sliding
scale technique. The dead time introduced by the ADC is
14
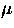 s; the number of bits for each channel is 16;
s; the number of bits for each channel is 16;
- High Resolution Time Profiles (HRTP): when the on-board trigger
is satisfied, time count profiles are stored independently for each of the four detectors and for any trigger occurring during an orbit and
transmitted with the following modality:
a) 8 s before the trigger time, with a time resolution of 7.8125 ms
b) 10 s from the trigger time, with a time resolution of 0.488 ms
c) 88 s starting from 10 s after the trigger time, with a time resolution of 7.8125 ms
The dead time needed to accumulate and store the data packets for each trigger is about 400 s.. This means that it is not possible to trigger an event occurring before 400 s after the former trigger.
The telemetry allocated to the GRBM allows to detect up to 12 events each orbit.
These data are transmitted to ground in a specific GRBM Direct Mode.
The first two data sets are used to extrapolate sources flux and spectral
properties (see following chapters); both raw and FOT data
are reduced using the PDS specific tools contained in the XAS package. The HRTP
can be used to perform temporal analysis of GRBs. The relative packets, containing also the
trigger time in OBT are present in the orbit per orbit PDS raw data set and
are provided to the GRBM hardware team in a specific FOT version. HRTP reduction and trigger
time conversion to UT is performed by specific programs developed by the GRBM group. The output of these dedicated programs is a set of ASCII light curves for each of the four LS and for each trigger.
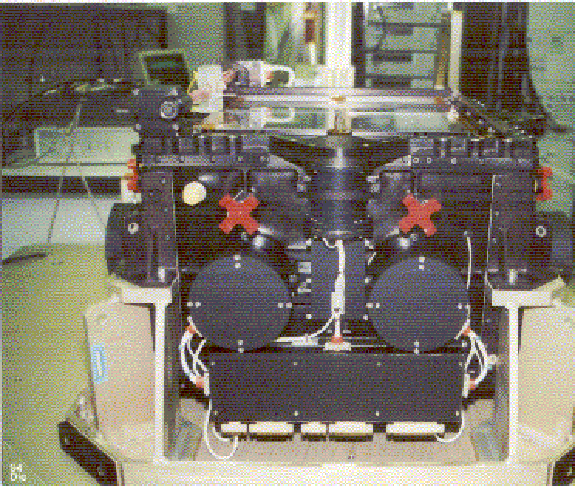
Figure 1.7:
PDS lateral shield view
 |




Next: GRBM on-ground calibrations
Up: The Gamma-Ray Burst Monitor
Previous: The Gamma-Ray Burst Monitor
Lorenzo Amati
8/30/1999
