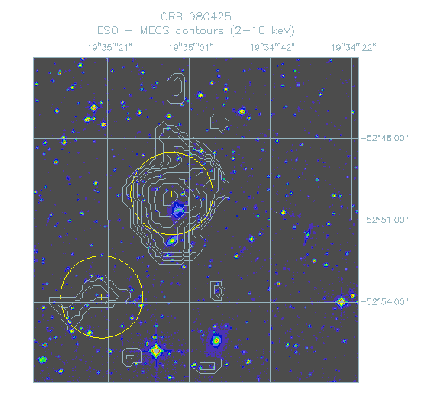
Another GRB which impacted significantly on the evolution of GRB science was the GRB980425. Not peculiar in any particular feature from the point of view of Gamma/X-ray
emission it had no outstanding afterglow source associated. A very faint source, not unlikely a field object was marginally detected only during the first 12 hours. This could be compared with the fading behavior of the well established X-ray afterglows and is the best "X-ray selected" candidate as the afterglow source. But the optical search following the X-ray position found a really unusual object. A Supernova (SN1998bw) with a very bright radio emission (5 times brighter of any radio SN previously known). The extrapolation to time 0 of the radio curve is coincident (![]() 1 day) with the GRB.
This could open the way to an entirely new perspective.
Is this the first finding of a separate class of GRBs or
is it a different phenomenology of GRBs observed from
a peculiar sight angle?
1 day) with the GRB.
This could open the way to an entirely new perspective.
Is this the first finding of a separate class of GRBs or
is it a different phenomenology of GRBs observed from
a peculiar sight angle?
 |